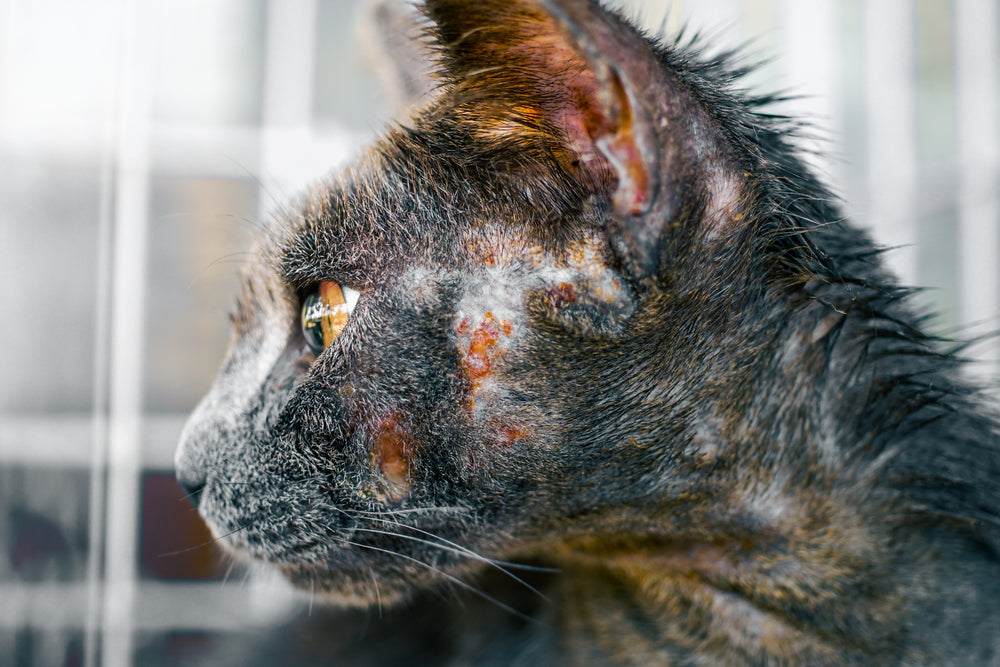
Fungi are living organisms that feed on organic matter, living or dead, and accelerate decomposition processes. When they infect cats, they can cause various skin conditions and become a common health problem. In addition, some fungi are zoonotic, meaning they can spread to people or other animals in the household.
For this reason, it is essential to learn to recognize the symptoms of fungi in cats, know their main types, and understand how to treat and properly prevent them to protect the health of your pet and the whole family.
Causes of fungi in cats
Fungi in cats usually appear when the animal comes into contact with contaminated people, animals, or objects. The likelihood of them causing disease depends directly on the cat’s immune system status.
In some cases, a cat may carry fungi without showing symptoms or developing any disease, but it will still be a carrier and able to spread it to others. Immunocompromised cats (very young, elderly, or sick) are especially vulnerable to fungal infections.
Main diseases caused by fungi in cats
Fungal infections mainly affect the skin, coat, and nails. They can appear in any area of the body, although they are most commonly found on the back, head (especially ears), tail, and legs. These are the most frequent:
Ringworm
Caused by the fungus Microsporum canis, it is highly contagious to both other animals and humans. Its spores can remain active in the environment for a long time.
Common symptoms: circular hair loss, flaking, dryness, and itching.
Malassezia
Caused by the yeast Malassezia pachydermatis, which is normally present on the skin. Only when the immune system is weakened does it proliferate and cause disease.
Common symptoms: hair loss, redness, flaking, and itching.
Cryptococcosis
Caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans, which is found in areas with bird droppings. Infection occurs through inhalation of spores.
Common symptoms: facial inflammation, nasal bleeding, coughing, sneezing, difficulty breathing, subcutaneous granulomas, and in advanced stages, seizures or vision loss.
General symptoms of fungi in cats
Although each infection presents specific signs, there are common symptoms that are often repeated in most cases:
-
Localized or generalized hair loss
-
Constant itching
-
Redness and skin irritation
-
Appearance of scaly areas or scabs
-
Poor coat condition
If any of these symptoms are detected, it is essential to visit the veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How to prevent contagion and fungi in cats
Some fungi, such as Microsporum canis, can spread to other animals and even people. Therefore, in addition to treating the infected animal, it is important to maintain strict hygiene in the environment:
-
Wear gloves when handling your cat and wash your hands thoroughly afterwards.
-
Wash all fabrics your cat has touched (beds, blankets, etc.) in the washing machine.
-
Frequently vacuum up your pet’s hair.
-
Disinfect the home and your cat’s belongings (toys, feeders, litter boxes, etc.) with bleach or other fungicidal products.
In addition, to prevent new infections, it is essential to keep your cat’s immune system strong:
-
Provide a healthy, complete, and balanced diet.
-
Schedule regular check-ups with the veterinarian.
-
Maintain good hygiene of their skin and coat. You can use specific products such as Smiley Pet shampoos and conditioners for cats, which are vegan, sulfate-free, and made with Dead Sea salts with repairing properties.
Fungi in cats are a frequent but treatable problem if detected in time. Recognizing the symptoms, promptly visiting the veterinarian, and maintaining a routine of hygiene and prevention are key to ensuring your pet’s health and avoiding contagion in the household.
With proper care and specific products, your cat will be able to recover quickly and regain a healthy, shiny coat.